Explore the intricacies of Apple’s AirTag Location History in our comprehensive guide. Understand how AirTag Location History works with the Find My network for tracking personal items, learn about their privacy features, and discover how they balance user convenience with security concerns. Ideal for tech enthusiasts and everyday users alike, this article demystifies AirTag’s capabilities and limitations in location tracking.
This overview also aims to shed light on the crucial aspect of privacy and security, core elements in the design and functionality of AirTags. With growing concerns about digital privacy, understanding how AirTags maintain user confidentiality, especially in terms of location tracking and history, becomes imperative. The introduction explores the balance AirTags strike between advanced technology and ethical responsibility, ensuring users can track their items without compromising their privacy.
As we navigate the functionalities and benefits of AirTags, this introduction serves as an essential guide for anyone curious about modern tracking technology, its applications, and its implications in our daily lives. It’s a journey through the intersection of technology, privacy, and convenience, showcasing how AirTags are revolutionizing the way we keep track of what matters most.
How to See AirTag Location History?
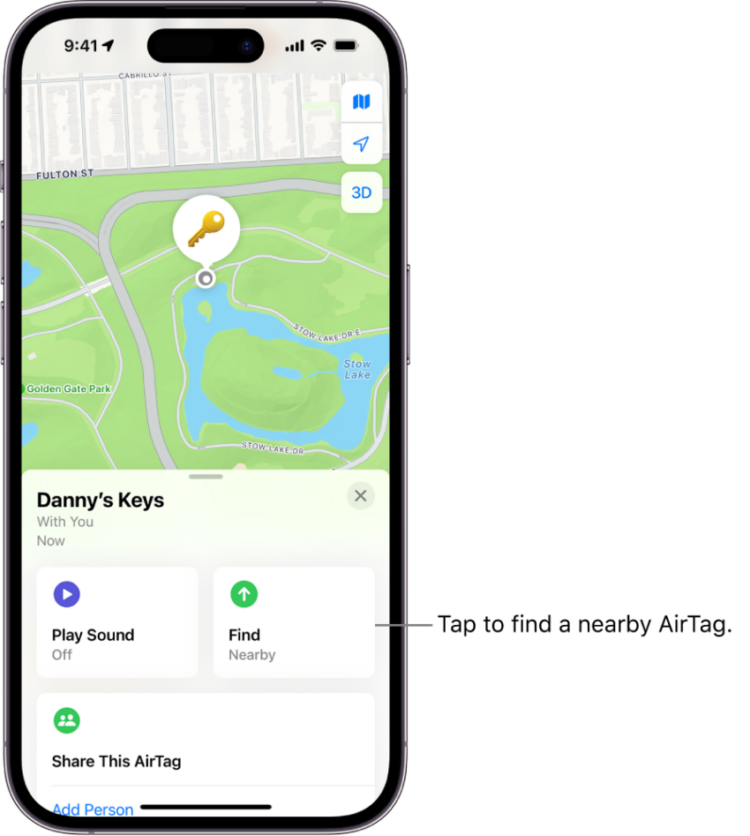
To see the location history of an AirTag, you need to use Apple’s Find My app, which is available on devices like the iPhone, iPad, and Mac. When you open the app, you’ll see a list of devices and items that are connected to your Apple ID, including any AirTags you’ve set up. By selecting an AirTag from the list, you can view its current location on a map.
However, it’s important to note that AirTags don’t store location history on the device itself. This means you cannot view a detailed history of all the places the AirTag has been, unlike some other tracking devices. What you can see in the Find My app is the AirTag’s last known location when it was in range of your device or another device in the Find My network.
If you lose an item with an AirTag attached, you can put the AirTag into Lost Mode via the Find My app. When in Lost Mode, if the AirTag comes within range of a device in the Find My network, you will receive a notification of its location. You can also opt to have the AirTag display a message with contact information if someone finds it.
For those concerned about privacy, Apple has incorporated features into AirTags to prevent unwanted tracking. For example, if an AirTag that doesn’t belong to you is moving with you, your iPhone will notify you. Additionally, an AirTag that’s separated from its owner for a prolonged period will start making a sound to alert people nearby.
In summary, while AirTags provide a way to track the current location of your items and receive notifications if they’re found when lost, they do not offer a full location history feature. Their primary function is to help you find misplaced items or track the location of items in real-time within the limitations of the Find My network.
How Frequently Does an AirTag Refresh (Update) Its Location?
The frequency at which an AirTag updates its location depends on several factors, primarily revolving around its proximity to devices in Apple’s Find My network. Here’s a general understanding of how it works:
- Proximity to Apple Devices: AirTags don’t have GPS and rely on nearby Apple devices (like iPhones, iPads, and Macs) that are part of the Find My network. When an AirTag comes into Bluetooth range of one of these devices, it uses its internet connection to update its location.
- Movement and Location Changes: If the AirTag is moving or changes location, it updates more frequently as it comes into contact with different devices in the network. In densely populated areas where there are more devices, updates could be more frequent.
- Battery Life Considerations: Despite being designed to conserve battery life (which lasts about a year under normal usage), AirTags still need to balance this with location update frequency. This means they won’t update constantly but will do so periodically to provide a balance between accuracy and battery conservation.
- Lost Mode: If an AirTag is put into Lost Mode, it will send out a secure Bluetooth signal that can be detected by nearby devices in the Find My network. When this happens, you might receive more frequent location updates, especially if the AirTag is moving and passing by various Apple devices.
- Privacy Features: To protect privacy, the exact process and frequency of these updates are not transparently detailed by Apple. This is to prevent the misuse of AirTags for tracking individuals without consent.
Data Privacy Policies for Apple AirTags
Apple has implemented several privacy policies and features around AirTags to address potential privacy concerns, especially regarding unwanted tracking and data security. Here’s an overview:
- Anonymous and Encrypted Data: The interactions between AirTags and the Find My network are designed to be secure and private. Location data transmitted by AirTags is encrypted so that only the owner of the device can access it. Even Apple cannot view the location of your AirTag.
- No Location History on Device: AirTags do not store location history on the device itself. This means even if someone else gets hold of your AirTag, they cannot extract past location data from it.
- Unwanted Tracking Prevention: To prevent AirTags from being used for malicious tracking, Apple has incorporated features that alert users if an unknown AirTag is found to be moving with them over time. If your iPhone detects an unfamiliar AirTag traveling with you, it will notify you. After a certain period of time, if the AirTag remains separated from its registered owner, it will start emitting a sound to alert nearby people.
- Regular Audits and Updates: Apple continuously audits the performance of AirTags and has shown a willingness to update its firmware to enhance privacy and security. This includes adjusting the time window in which an AirTag will sound an alert if separated from its owner.
- User Consent for Location Access: The Find My app requires user consent to access location services on your device. This means you have control over whether or not your device can be used to help locate AirTags.
- Limited Data Collection: Apple states that they collect only the data necessary to provide the Find My service. This data is not used for marketing or advertising purposes.
- Family Sharing Considerations: If you’re part of a Family Sharing group, you cannot see AirTags associated with other family members unless they specifically share them with you in the Find My app. This respects the privacy of individual family members.

Conclusion
Apple’s AirTag represents a significant advancement in the realm of personal item tracking, offering users a convenient and efficient way to keep tabs on their belongings. However, it’s important to recognize that while AirTags excel in real-time location tracking, they do not provide a historical record of locations. This design decision is a reflection of Apple’s commitment to user privacy and security. Implementing features like encrypted and anonymous data, alerts for unwanted tracking, and the absence of stored location history on the device demonstrate Apple’s careful consideration of privacy concerns. Despite these limitations in location history, AirTags stand out for their integration with the expansive Find My network, ease of use, and innovative approach to helping users locate lost items. As technology continues to evolve, devices like AirTags will likely become even more sophisticated, potentially offering enhanced features while continuing to prioritize user privacy and security.